Workflow Example: Micro Focus OpsBridge (OMi) – BMC Remedy
Event Submission and Incident Creation
The CLIP Integration Platform enables the automatic or manual generation of BMC Remedy incidents (tickets) in response to events detected by OMi. So called “Forwarding Rules” can identify OMi events to be forwarded automatically without operator intervention. Events matching these rules are automatically forwarded and create incidents in BMC Remedy. For example, an IT organization may require an incident be opened for critical, major or root cause events.
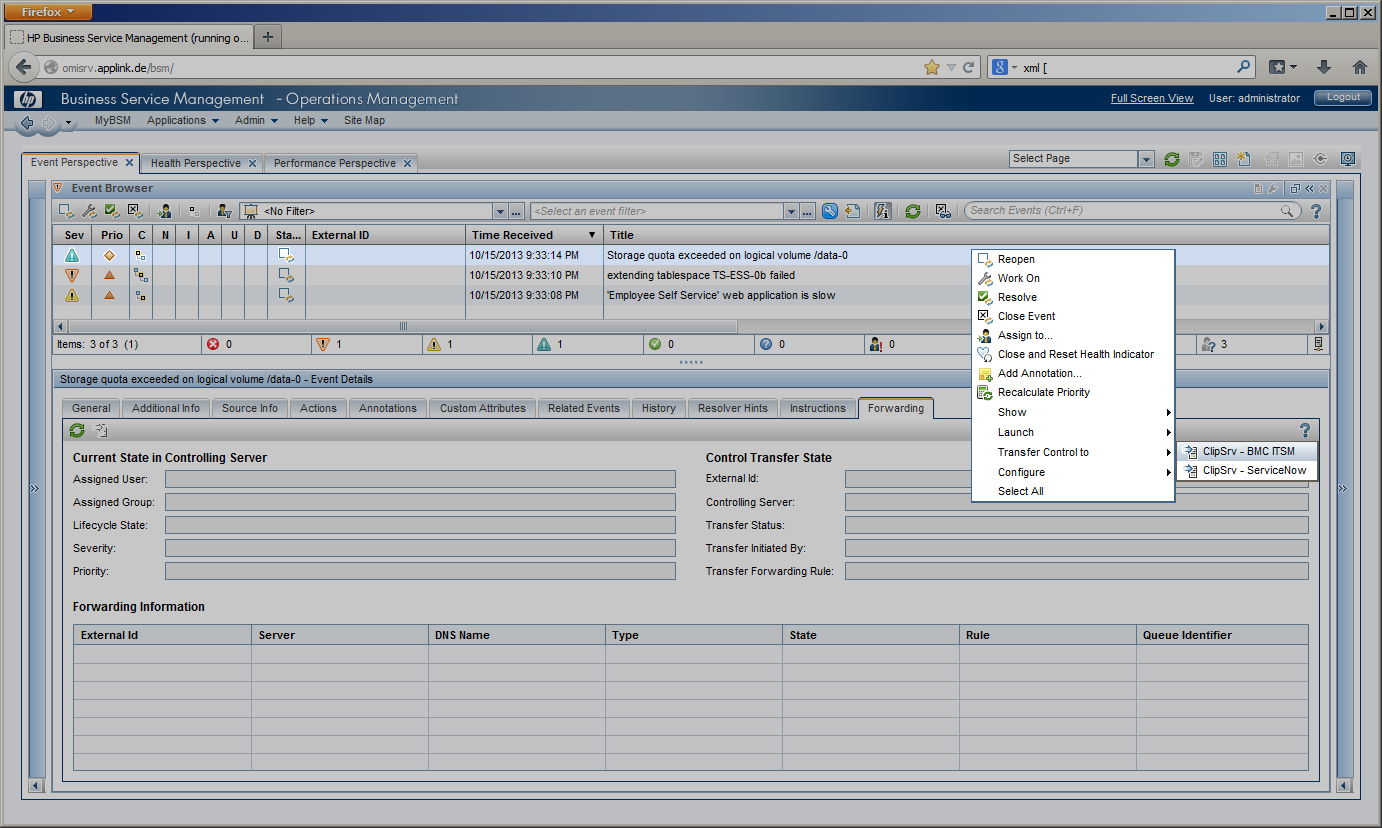 |
Alternatively, an OMi Operator can select an event in the OMi “Event Perspective” and use the menu option “Transfer to …” to create an incident manually. | |||
|
Incident Creation |
 |
|||
|
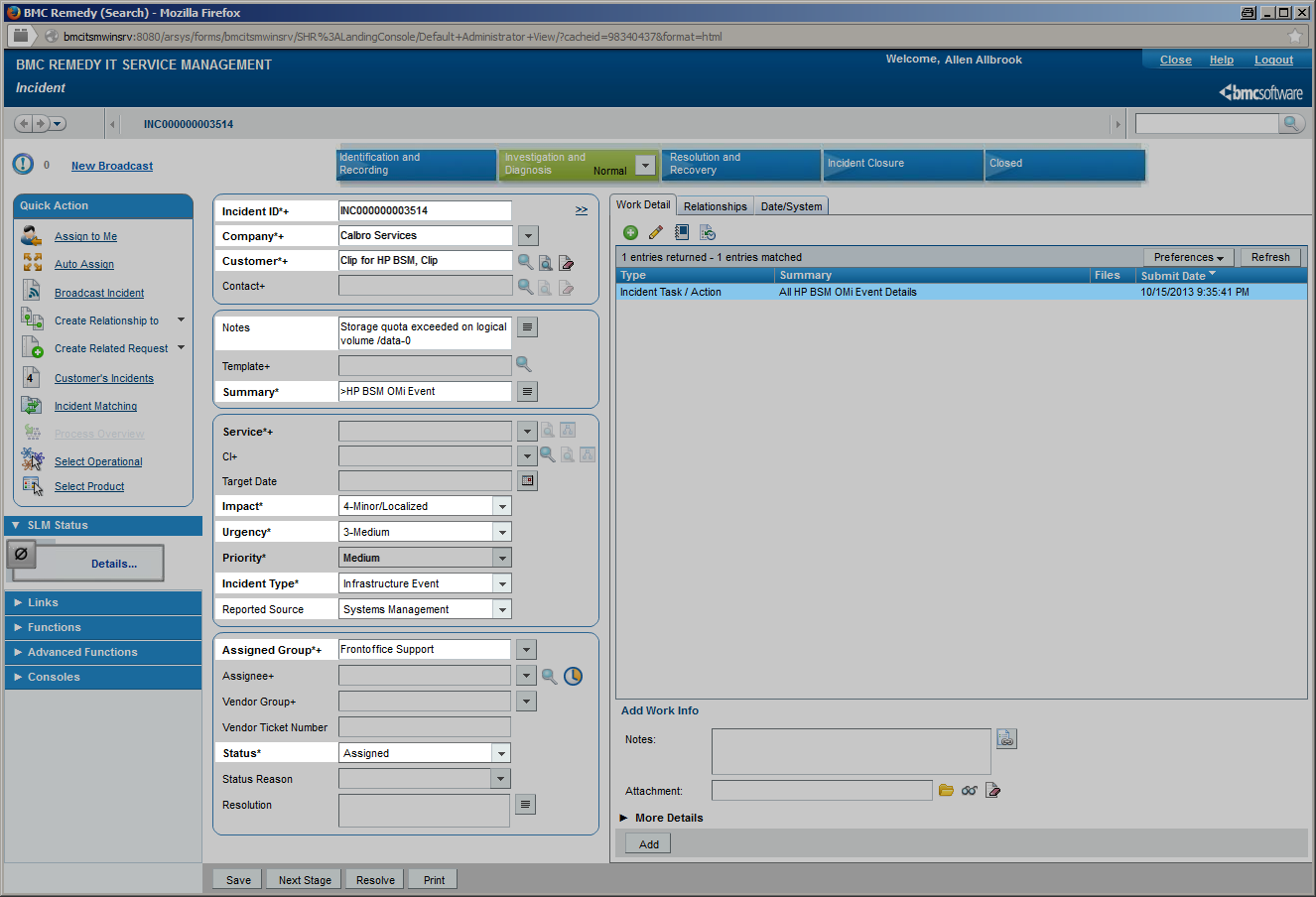
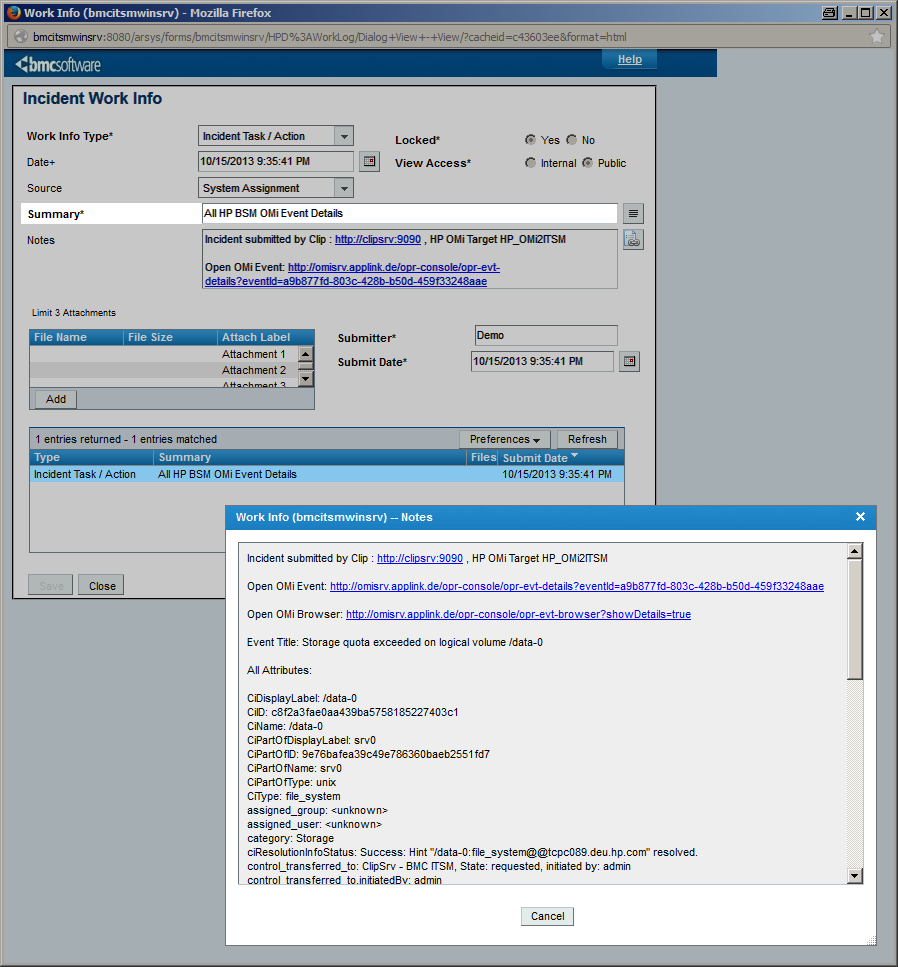
Once CLIP has received an OMi event, it extracts all available event attributes to make them available for incident creation. Each available field in the BMC Remedy submission form can be configured individually to be set to a static value, one or more event attributes or a combination of all. Conditional assignments of field values allow for the setting of different field values depending on the current event attribute values: an event of “critical” severity can create an incident of urgency “High” whereas a “major” event can cause an incident of urgency “Intermediate”. CLIP automatically converts field values into the correct data types and takes field length restrictions into account. On the BMC Remedy side, CLIP provides an out-of-the-box configuration to integrate into the BMC ITSM Incident Management application and also a demo form for an instant preconfigured integration demonstrating CLIP capabilities. Customers using their own BMC Remedy Incident Management application can easily configure CLIP to integrate, or as an alternative, use the CLIP Demo form as a starting point for a BMC Remedy workflow that creates the final incident in the customer’s application.
|
||||
 |
||||
 |
Event Update | |||
Right after incident creation, CLIP optionally reads back the incident to retrieve incident attributes that were set by BMC Remedy workflow, such as:
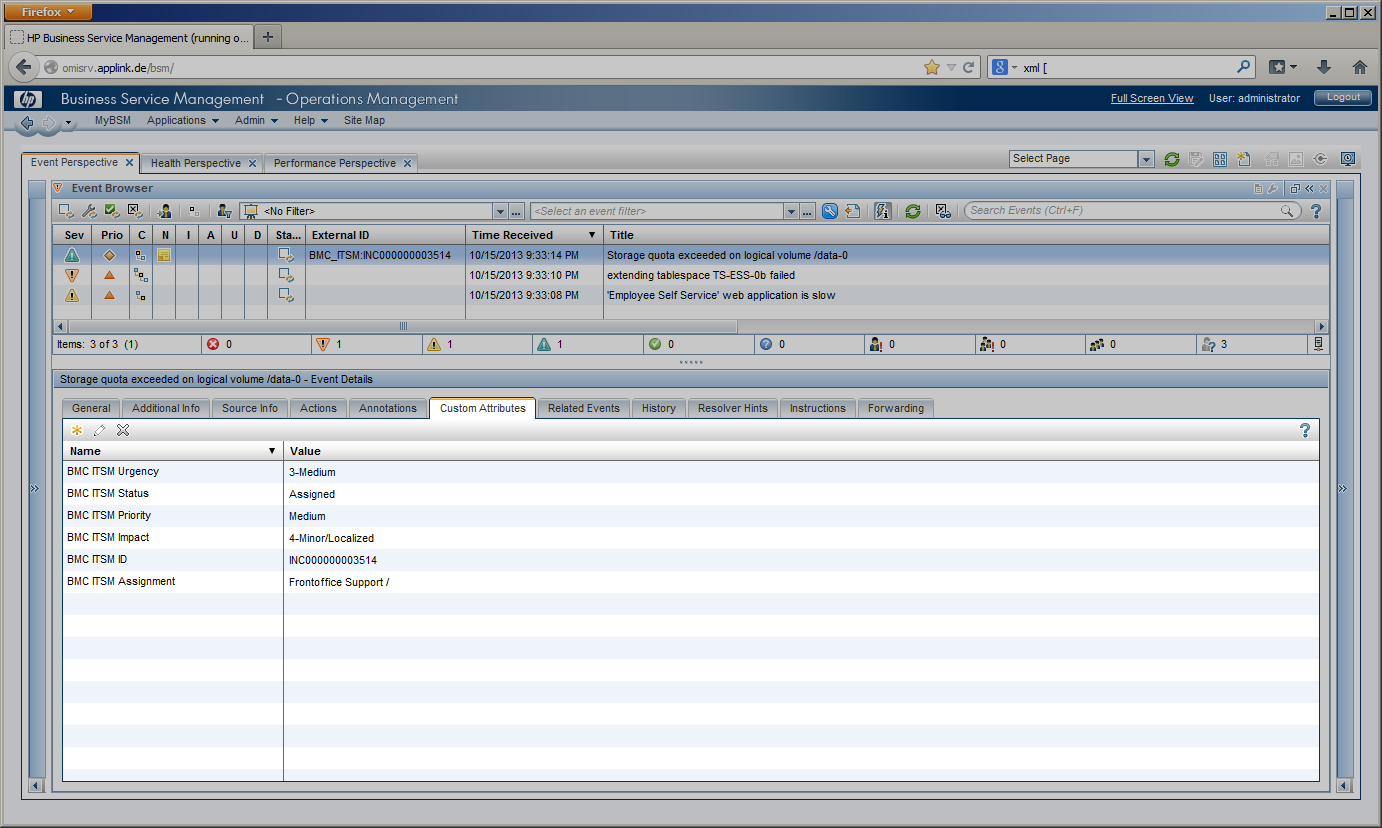
CLIP can update the originating OMi event to display relevant information about the BMC Remedy incident to the OMi operator in different ways:
In case CLIP is not able to create the incident, CLIP retries incident creation if the BMC Remedy Server is down or not reachable, or marks incident creation as “failed” in the CLIP GUI and the event’s annotation together with the reason.
|
||||
 |
||||
 |
||||
Bidirectional Update Processing
Once CLIP has created an incident, CLIP performs a bidirectional synchronization between the incident and its originating OMi event: modifications of the originating OMi event can cause the BMC Remedy incident to be updated (forward synchronization) and modifications of the BMC Remedy incident can cause updates of the OMi event (backward synchronization).
Forward Synchronization |
Backward Synchronization |
|
| Once CLIP has received an event modification from OMi, CLIP extracts all available event attributes that have changed and can modify the related incident according to its configuration.
OMi event modifications available for forward synchronization include: |
If the BMC Remedy incident is modified, e.g. a Service Desk User has been assigned, the priority has changed or a work log entry has been added, CLIP can modify the OMi event, e.g. by adding annotations or custom attributes, changing its severity, etc.
BMC Remedy incident modifications can change the following OMi event attributes: |
|
|
|
Example Process flow and the lifecycle of an OMi event and BMC incident request
The following examples show possible update scenarios of the originating OMi event and the corresponding BMC Remedy incident while they pass different lifecycle stages.
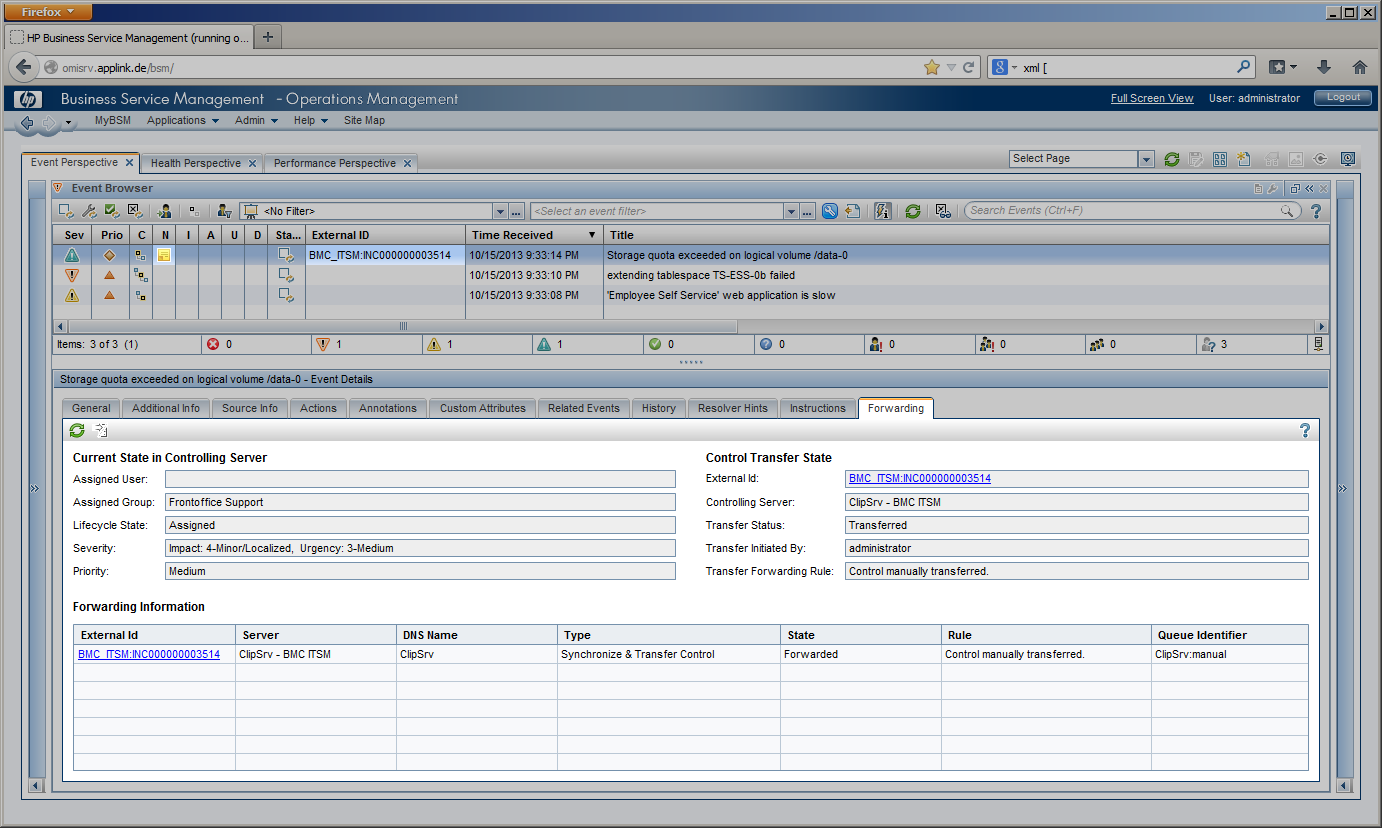
| Once a BMC Remedy incident has been created by CLIP, it changes its lifecycle stage from “Identification and Recording” to “Investigation and Diagnosis” until it is resolved by the service desk staff ( “Resolution and Recovery” ). The final stage, “Incident Closure”, is reached as soon as the resolution has been accepted by the Service Desk customer. | 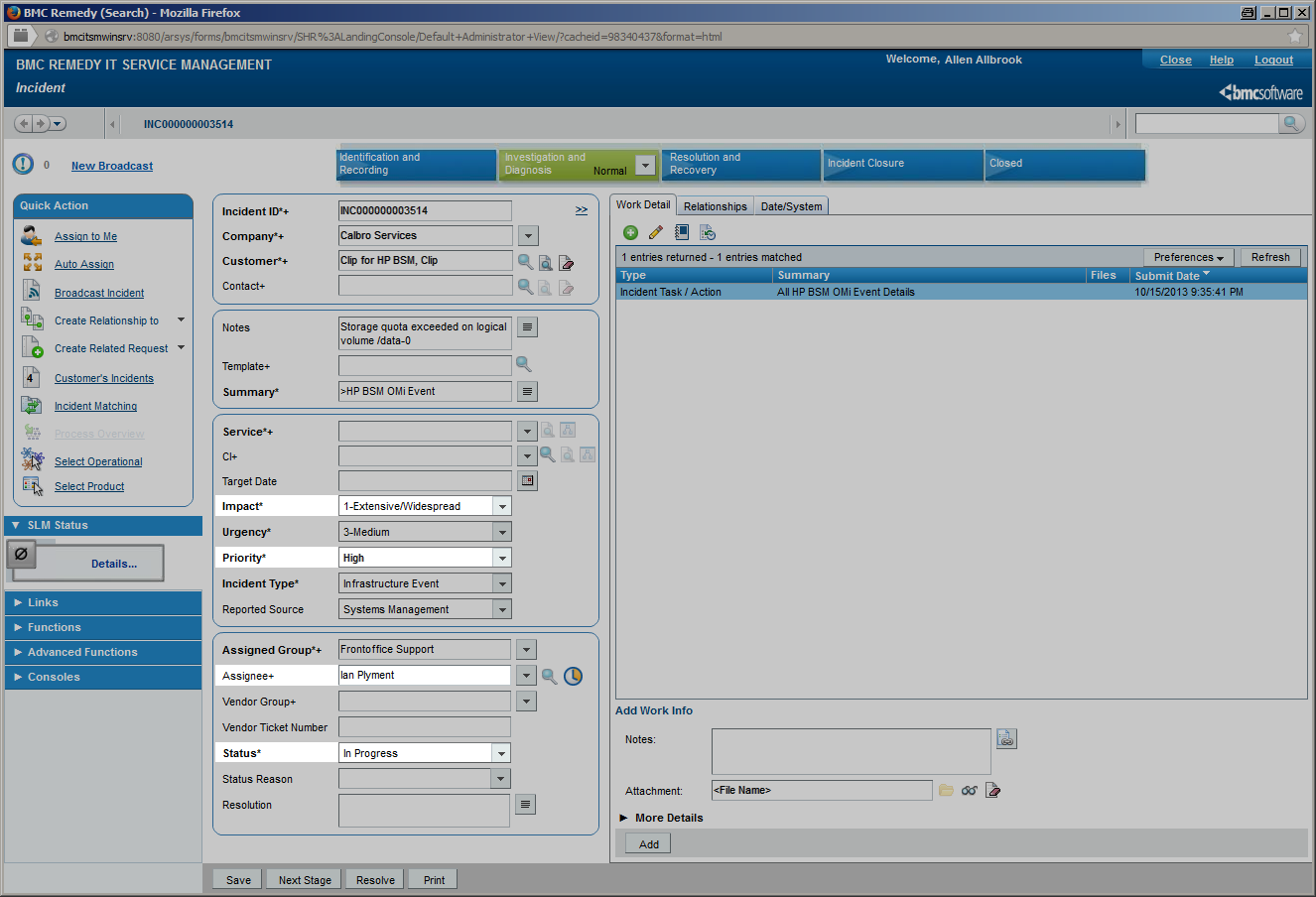 |
|||
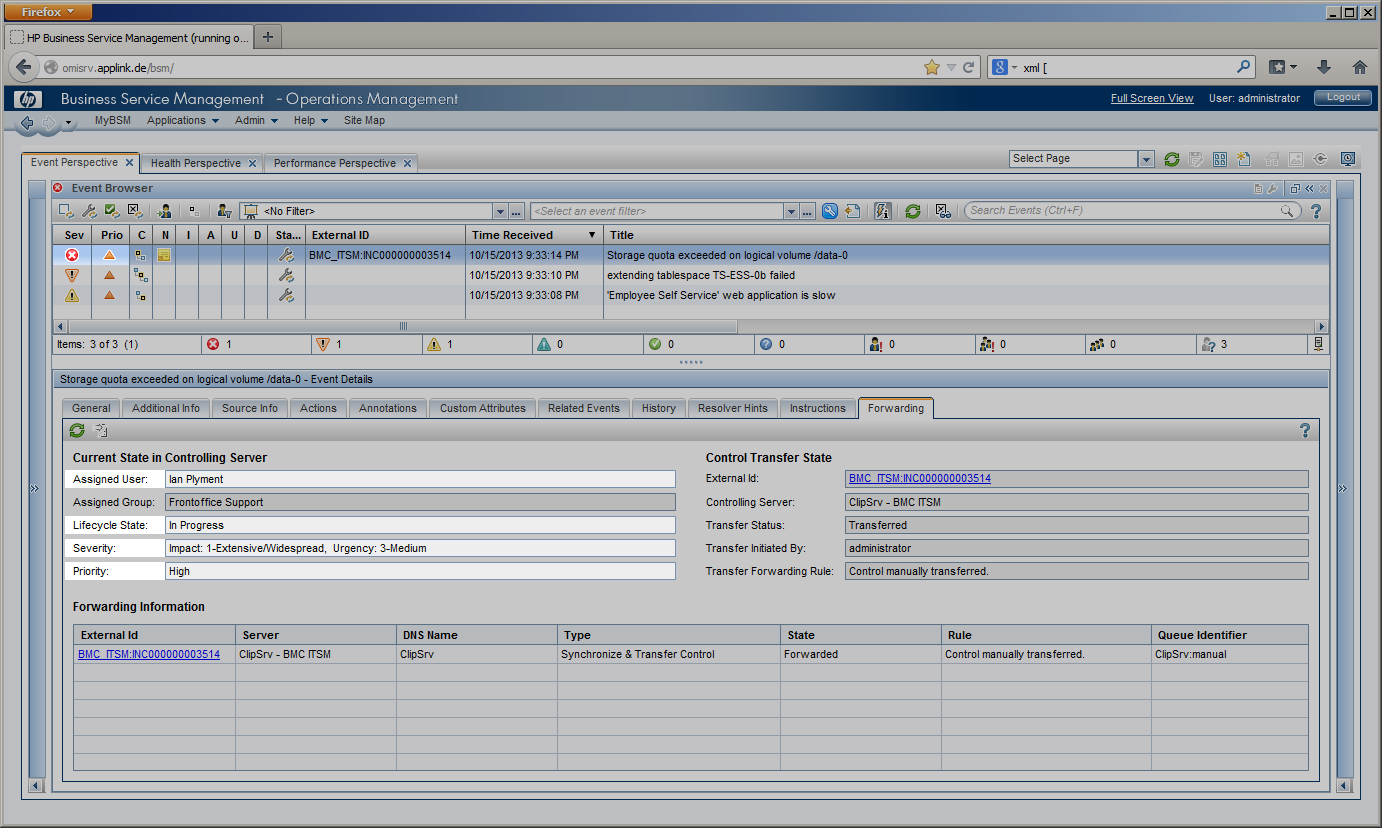 |
Incident Update |
|||
|
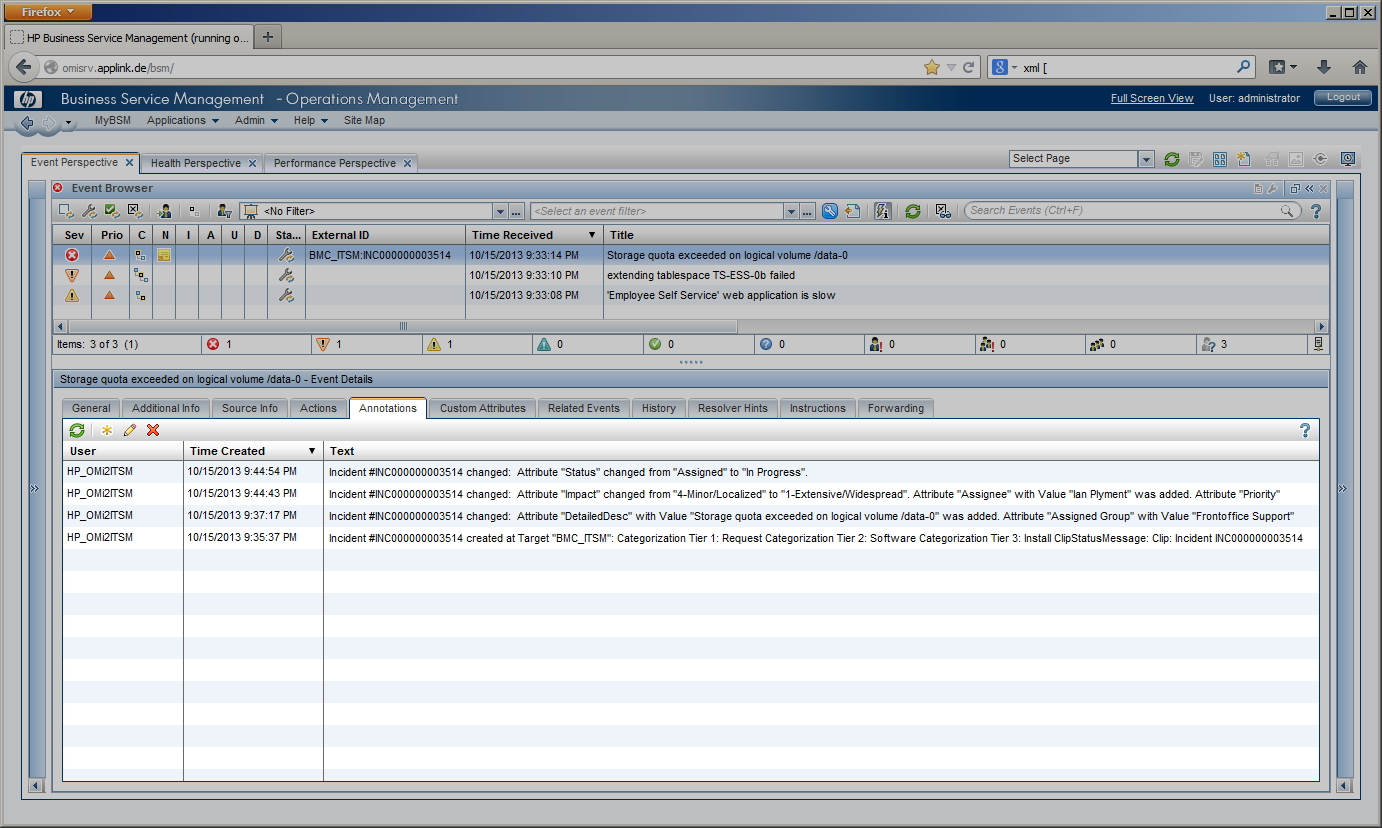
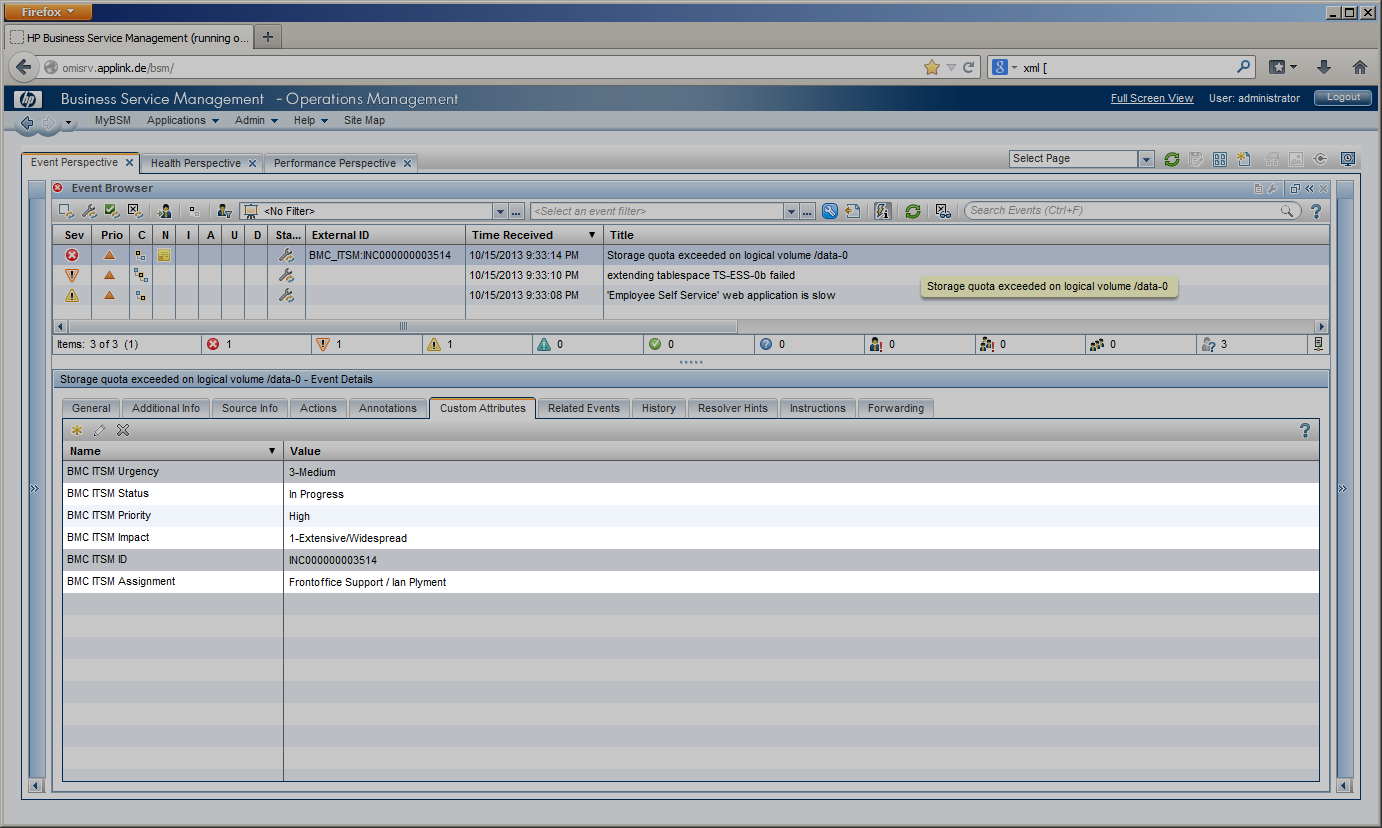
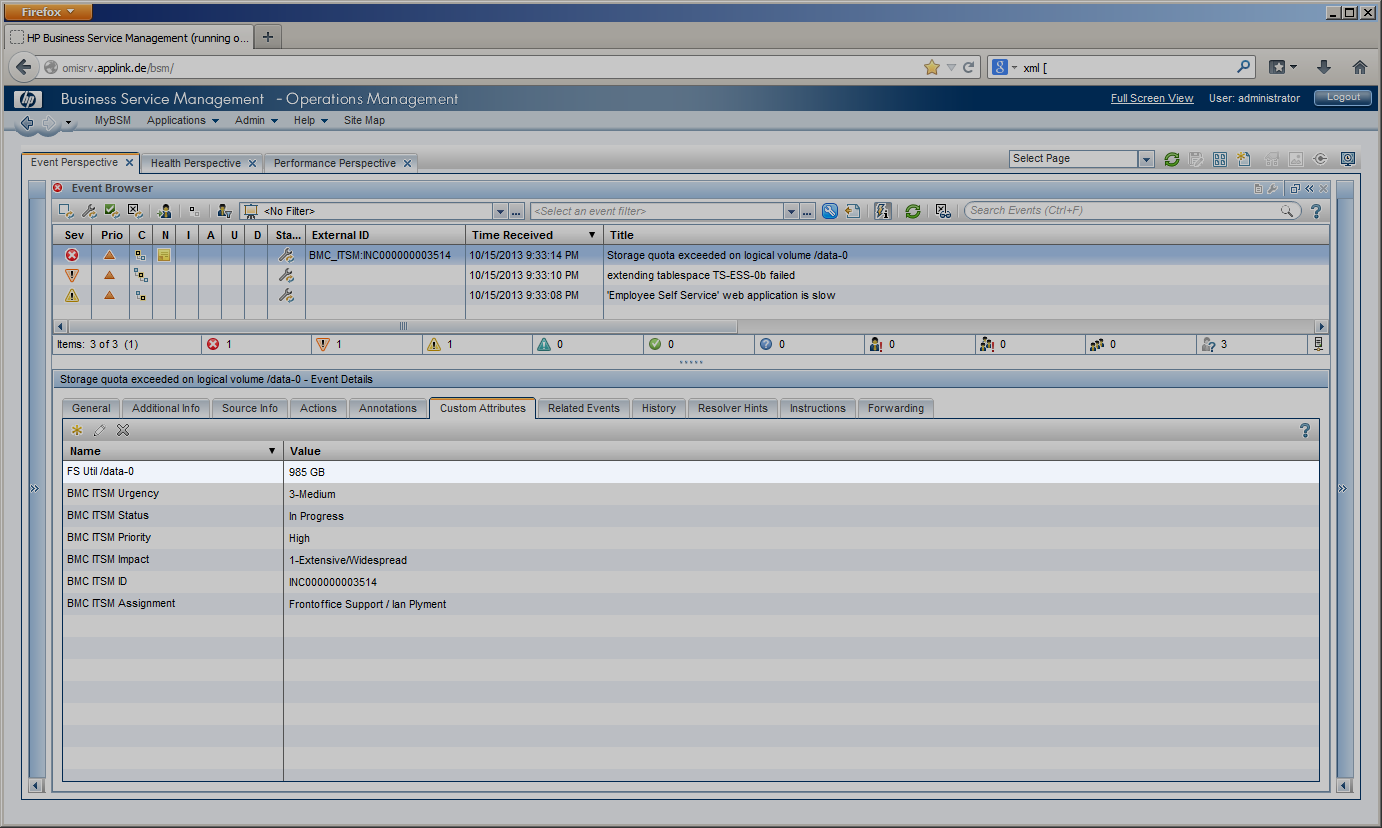
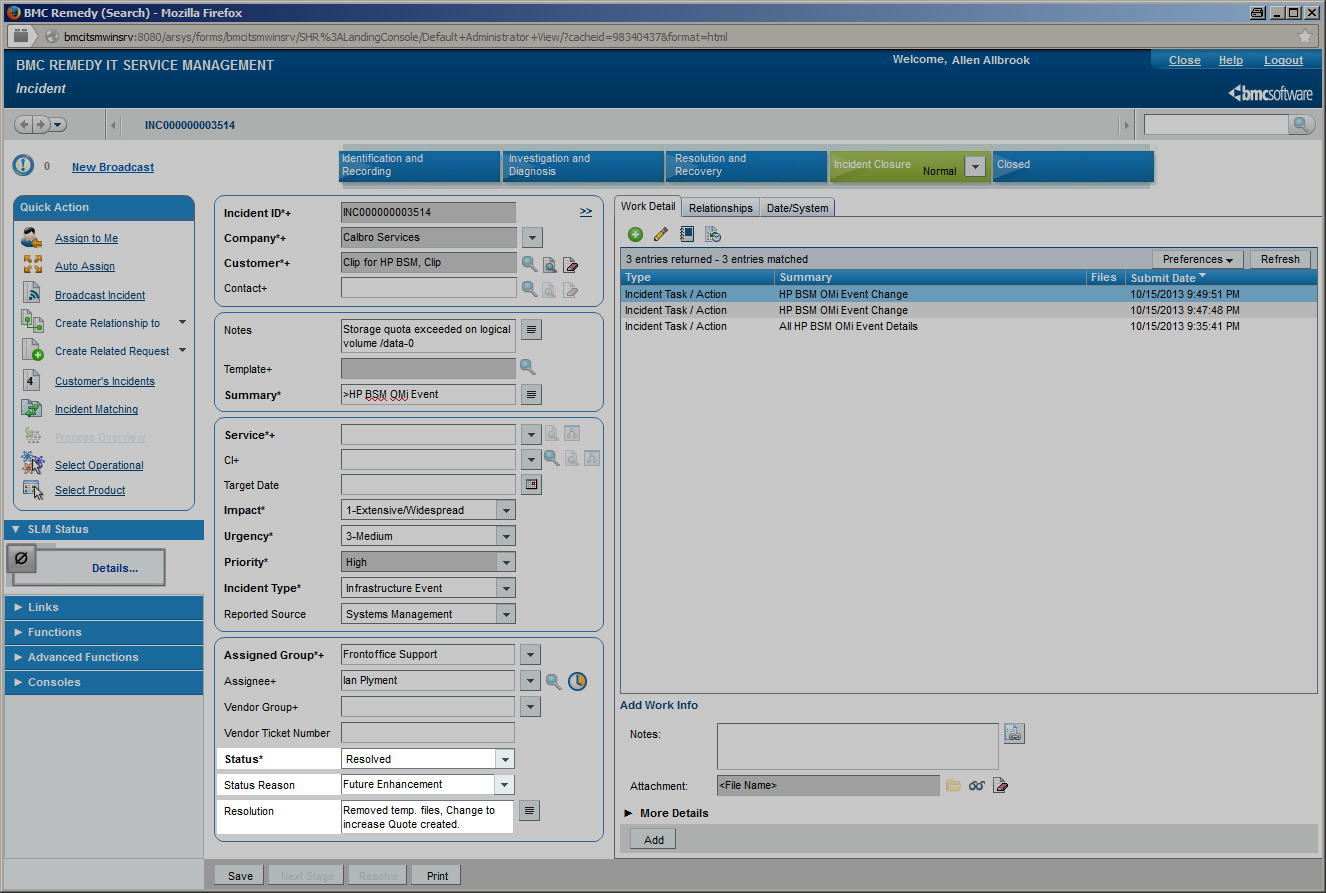
During these lifecycle stages, the assignment of the incident can change, a first-line Service Desk analyst might assign the incident to a different Support group or a second- or third-line specialist. The current lifecycle stage is reflected in the incident’s state and changes from “Assigned” to “In Progress” while the service desk staff is working on the incident before it is “Resolved” and finally “Closed”. Impact, Urgency and Priority of an incident may be changed while investigating the incident. In the example given, Impact has been set to “Extensive”. All these incident modifications are instantly visible to the OMi operator in several ways. The OMi severity is changed to “Critical” in this example according to the mapping rules configured in CLIP, while the OMi event state is modified to “In Progress”. The “Forwarding” Tab in OMi gets instantly updated to display the current incident values for Assignment, Lifecycle State, priority and severity. An event annotation can be added any time an incident is modified listing all modifications of the incident. OMi event’s custom attributes can contain relevant incident attributes such as incident ID, Status, Urgency, Impact or the assigned team / assignee. |
||||
 |
||||
 |
||||
 |
Also OMi Events pass through a “lifecycle,” which is an informative way to display and monitor the status of an event. An OMi operator’s workflow is based around the lifecycle of an event. The lifecycle state of an event represents the progress of the investigation into the problem that caused the event. An operator assigned to an event opens an investigation and works on finding a solution to the event’s underlying problem. Experts can then assess the proposed solution, verify that it solves the problem that caused the event and close the event, which completes the lifecycle. | |||
|
Event Update |
 |
|||
|
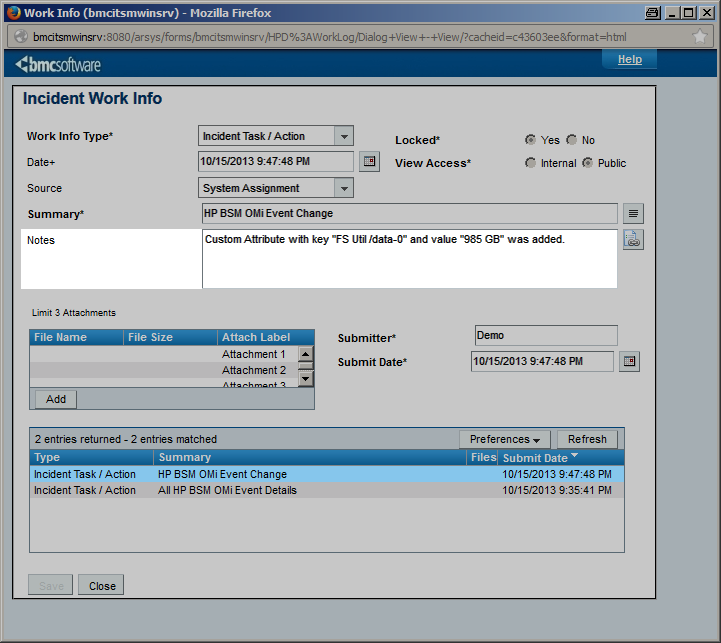
While the OMi event passes through its lifecycle stages, it can be modified in different ways. As an example, an automatic action might add or modify a custom attribute which is then forwarded to CLIP to add an additional “Work Info” entry to the corresponding incident. |
||||
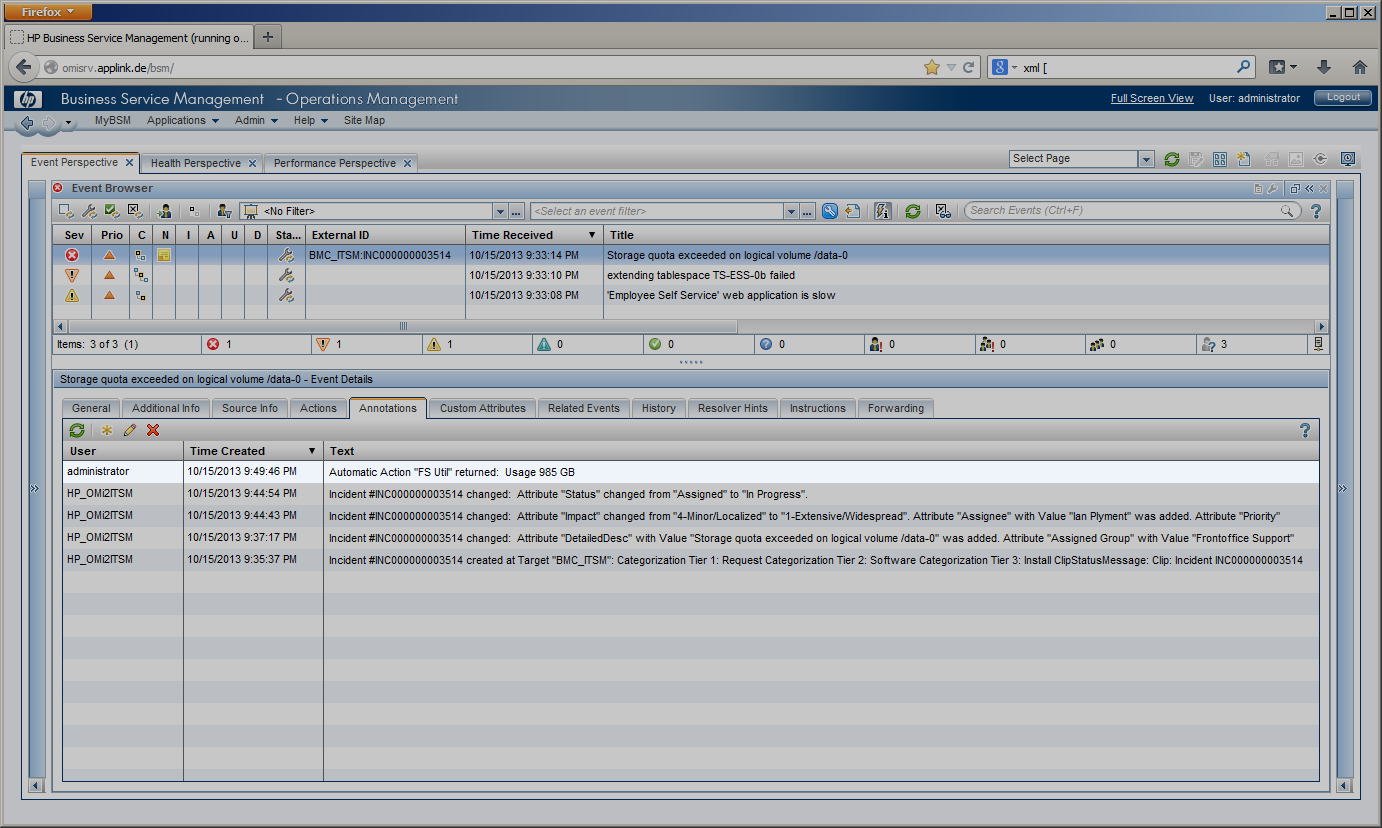 |
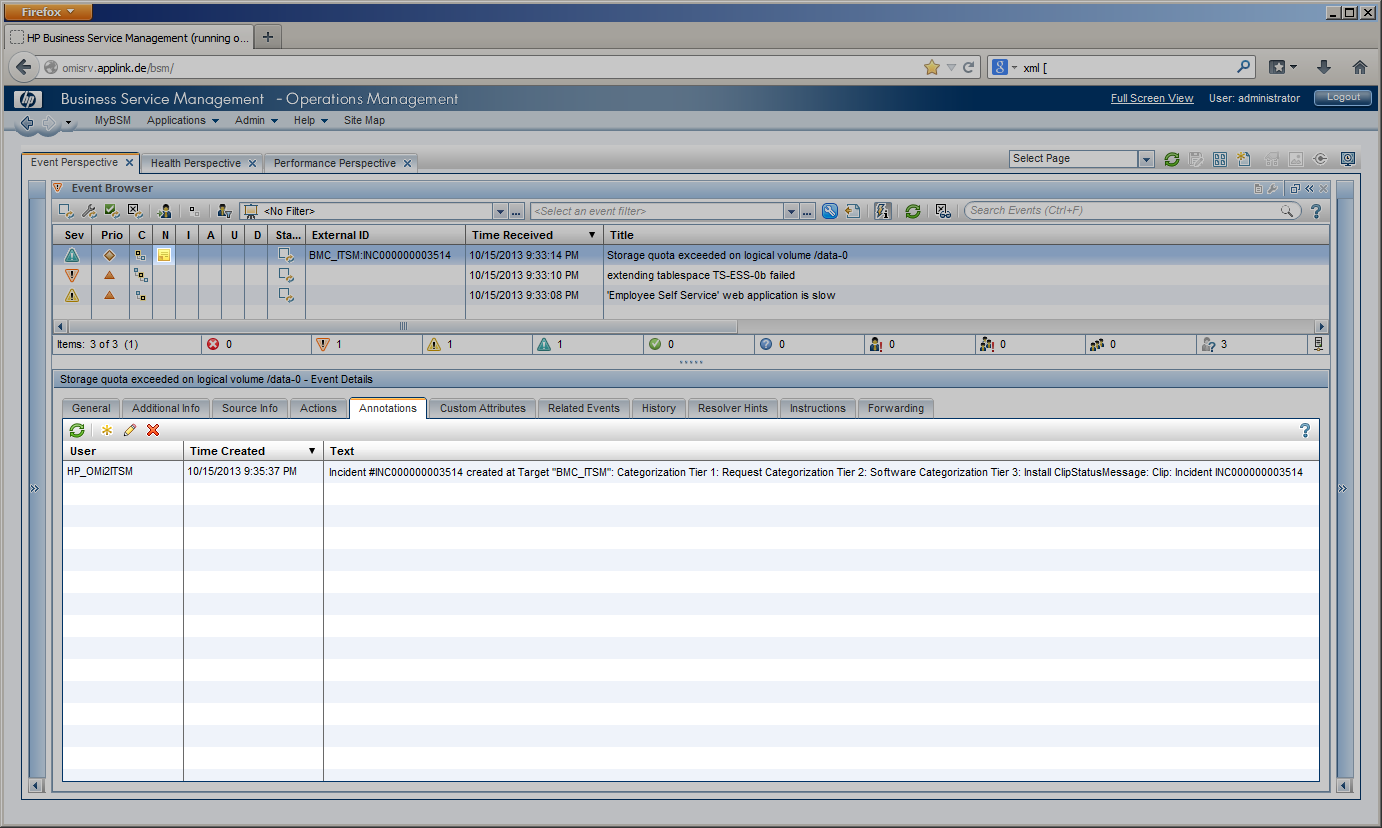
OMi Operators can enrich events with additional information, for example, by adding annotations to the event to either aid further problem resolution or to document what action has already been taken.
Additionally, preconfigured automatic actions can gather further information about the problem or even try to automatically resolve a problem and add annotations to the event. |
|||
|
Event Update |
 |
|||
|
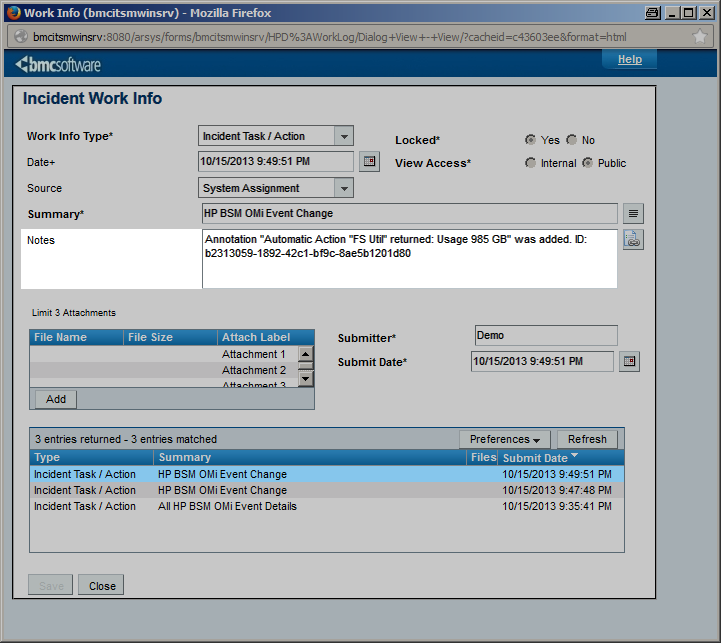
Added OMi annotations can be forwarded to CLIP to add additional work log entries to the BMC Remedy incident. |
||||
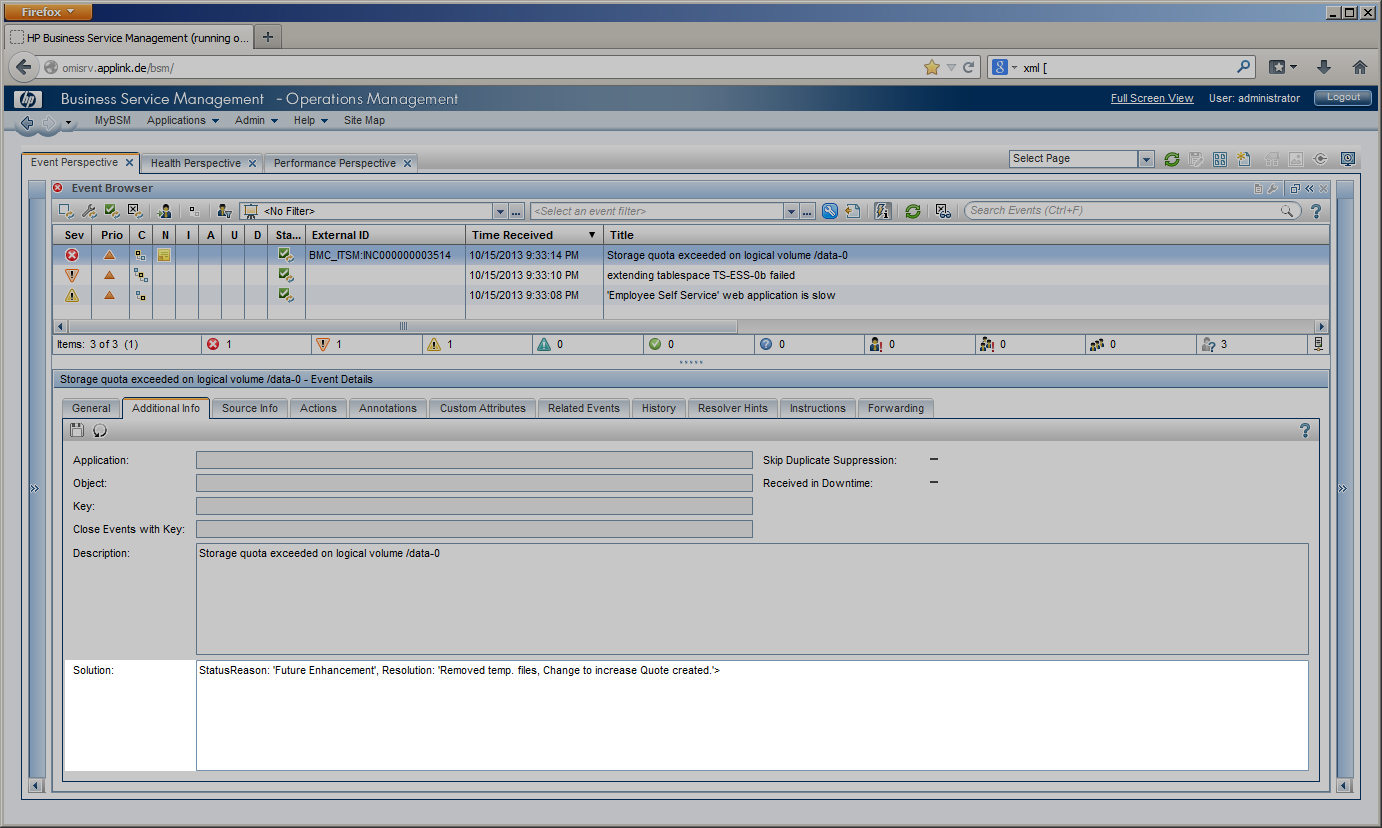
| Once an incident has been resolved, the incident’s “resolution” field is filled out and describes the steps that were required to resolve it. The “Status Reason” field can indicate action required before the incident is closed, such as “Customer Follow-up Required” or “Future Enhancement”. |
 |
|||
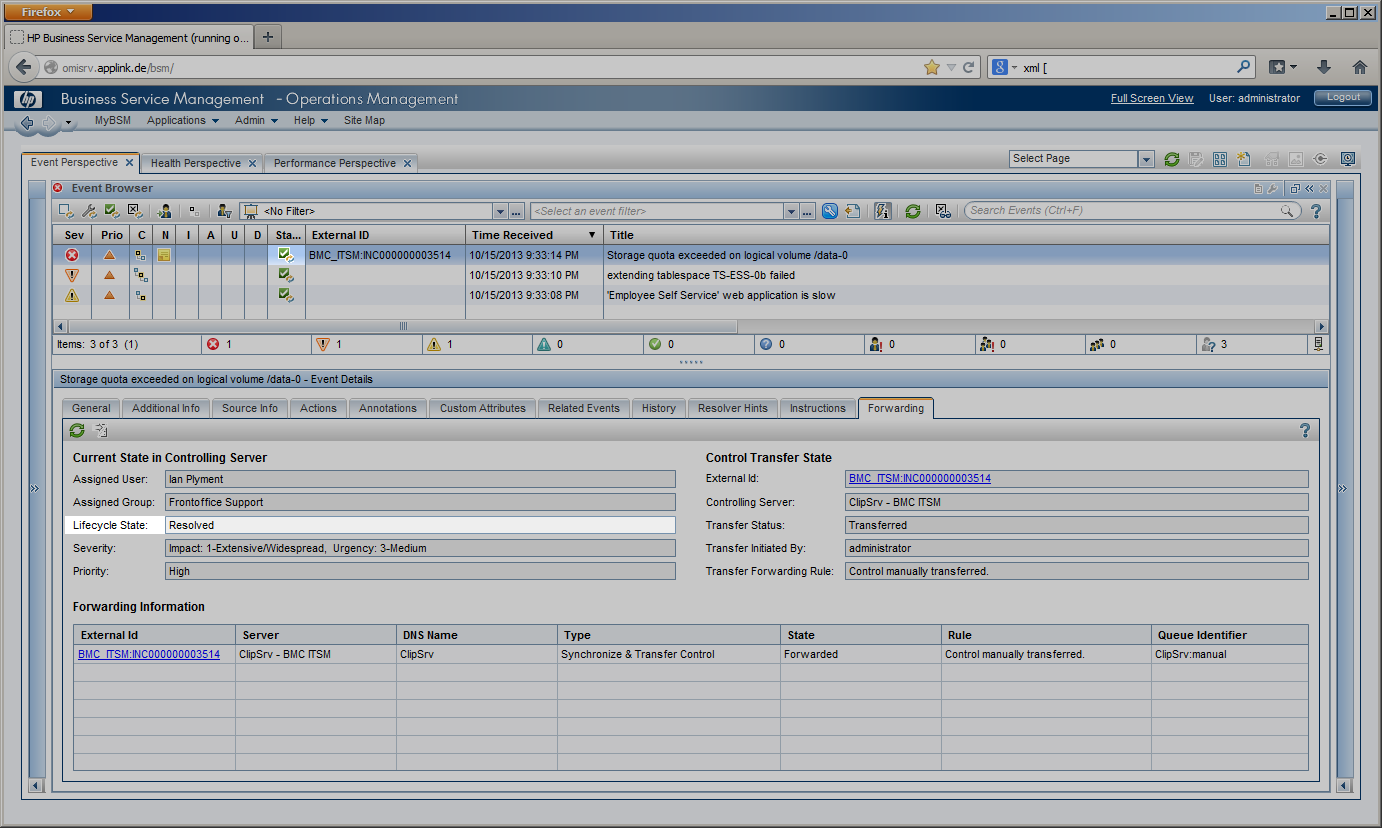 |
Incident Resolution |
|||
|
On incident resolution, CLIP updates the corresponding OMi event:
|
||||
 |
||||
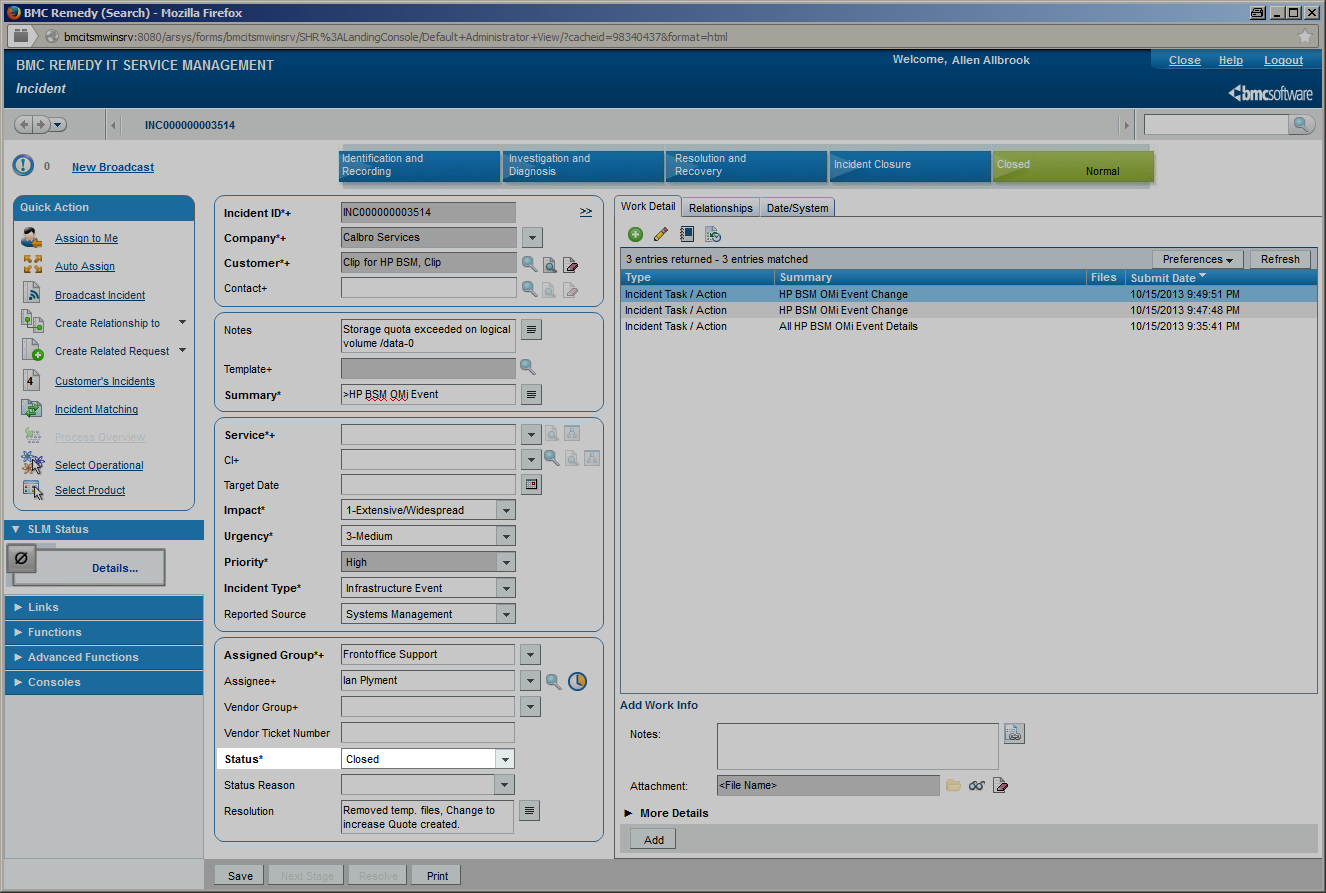
Event and Incident Closure
| The synchronization process performed by CLIP can be terminated when either the event is closed on the OMi side or the incident is closed on the BMC Remedy side. In both cases, actions like automatic closure of the peer event or incident can be performed. |
 |
|||
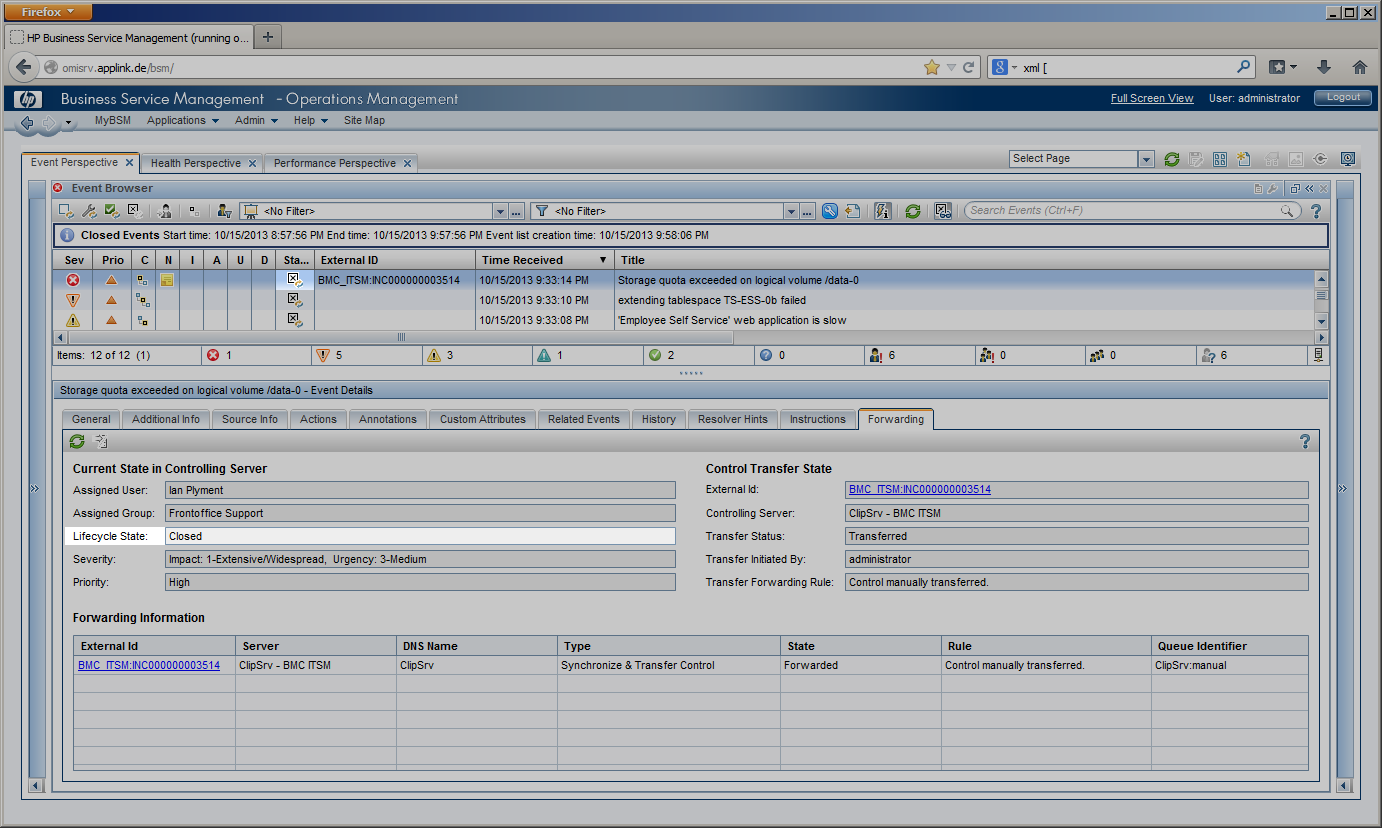 |
Incident Closure |
|||
|
The OMi event displays the incident’s “closed” state in the “Forwarding” Tab. Once its state is set to “closed”, it moves to the “Closed Events” view in OMi. Even though the synchronization performed by CLIP is finished, all the actions performed, such as event reception, incident creation and all updates on the event and the incident, can be reviewed in the CLIP web interface. |
||||
Configuration Tasks
To achieve a standard integration as described above, minimal configuration steps need to be performed.
In OMi, a “connected server” needs to be configured that contains the information about how OMi should submit events and event changes to CLIP to finally create and modify incidents. The “connected server” contains information such as the system name running CLIP, the URL to post events and event changes along with the credentials to log into CLIP.
On the BMC Remedy side, preconfigured “filters” need to be imported to synchronize incident changes back to OMi so CLIP can modify OMi events according to its configuration and current incident attributes.